Dacheng Zhang, Data Storage Resilience Technology Expert of a Large IT Company
In recent years, the mining of data has been accompanied by a surge in malicious attacks. This has prompted the storage industry to prioritize data resilience as a core capability. Recent market feedback reveals growing user recognition of ransomware protection on the storage side. Notably, storage encryption is gaining traction as a compliance solution that delivers high performance without requiring service transformation. By using immutable snapshots and backup copies—key measures on the storage side—this solution ensures the recovery of critical data. Storage resilience solutions are becoming an increasingly indispensable component of in-depth cybersecurity systems, complementing the network and host resilience solutions that currently dominate the market.
Where should storage data resilience go next? How can we maximize storage technologies to enhance data resilience solutions in the era of growing data value? With these questions in mind, I have gathered reflections from my practical experience and hope to offer valuable insights into these topics.
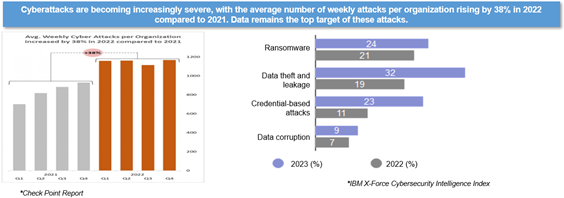
Reports from security companies such as Splunk and Check Point Software reveal a sharp surge in data-targeted attacks in recent years, driven by the mining of data. In 2022, the number of attacks per organization per week rose by 38% year-on-year, with a significant proportion aimed directly at data. Notably, 79% of enterprises experienced ransomware attacks over a two-year period, with 35% of these incidents impacting both data and services. As attacks continue to increase annually, resilience solutions focused solely on the network and host levels are struggling to address the growing complexity of these threats.
Against this trend, there is an increased exploration of the potential of storage in safeguarding data. Key technologies include disk data encryption to protect data confidentiality, ransomware detection and recovery to ensure data availability and integrity, as well as WORM, secure snapshots, disaster recovery, and archiving solutions. Disk data encryption prevents data breaches in the event of storage media theft. Ransomware protection solutions identify potential attacks by detecting abnormal changes in data characteristics, such as entropy variations and deduplication or compression ratio shifts. Unlike network- and host-level resilience solutions, storage systems offer unique advantages in protecting data written to disks.
However, some users have questioned the value of storage resilience solutions. They argue that storage devices are typically deployed deep within the network, serving primarily as the 'last line of defense' in a protection system. By the time stored data is attacked, the attacker has likely already penetrated the network and gained access to critical nodes, such as servers or service systems. According to the Cyber Kill Chain theory, intercepting attacks earlier in the chain is more effective, as blocking an attack at its initial stages minimizes damage and losses, whereas later intervention often results in greater harm.
User doubts stem from traditional in-depth defense systems. These systems primarily focused on network protection while paying little attention to data protection. This approach is akin to securing a home filled with treasures by simply installing a sturdy front door, and leaving the valuables exposed on the table—making it easy for an intruder to take them once inside. However, as data becomes an increasingly critical asset and production factor, security design principles are evolving. Data protection measures must ensure that security policies align with the value of the data throughout its entire lifecycle. Since data is easily modified and replicated, inadequate protection at any stage of the lifecycle can result in significant data asset losses.
The role of storage in data resilience, often seen as a container for data, needs to be reevaluated. According to the Zero Trust theory, threats can originate from network boundaries or within an organization. Recognizing this, storage vendors are beginning to incorporate security features traditionally reserved for high-security systems into storage devices. One such example is multi-party authorization, which requires multiple administrators to approve any modifications to critical storage configurations. This shift highlights the industry's renewed focus on the strategic importance of storage in data resilience.
Looking ahead, the emphasis will increasingly be on comprehensive data lifecycle protection, coupled with enhanced security measures for storage devices. These advancements aim to better safeguard user data assets while ensuring data resilience and integrity.
Here are my thoughts on the future directions of storage data resilience.
Direction 1: Expanding the scope of ransomware protection in storage solutions
This means deploying detection and protection measures upfront, at the earlier stages of the Cyber Kill Chain. Security capabilities of hosts and the network are combined to safeguard data before a breach occurs. Two practical approaches can be used to achieve this objective:
Approach 1: Building an in-depth, multilayered defense system that integrates network, storage, and compute resources to enable seamless security information analysis and collaboration across networks, hosts, and storage systems.
In practice, the storage system reports detection results to a security situational awareness system for analysis. If potential attacks are identified on the network or host side, the security system can prompt the storage system to take protective actions, such as creating snapshots or backups to safeguard critical data, or isolating the backup system from the production system to prevent intrusion into backup resources. Currently, storage vendors in North America are developing a security ecosystem that unifies measures across storage, network, and computing (host) layers. This integration enhances cybersecurity situational awareness and strengthens data loss prevention (DLP) solutions.
Approach 2: Deploying a private storage client on the host to detect potential attacks targeting the host. The client collects host information, such as a process's access to data, and transmits it to the storage system to establish a behavioral baseline. This is then combined with data characteristic change detection within the storage system, creating an enhanced security monitoring mechanism.
When a potential attack on the host is identified, the storage system can take measures such as creating secure snapshots or initiating I/O-level continuous data protection (CDP). Additionally, it alerts administrators to take corrective actions. This concept is already being explored by some vendors. For instance, in storage backup solutions, a backup agent is often deployed on the host to facilitate data backup. A number of backup vendors are using this agent not only for backups, but to monitor host security status. Some are even going a step further by deploying honeyfiles on the host to improve attack detection capabilities.
Direction 2: Exploring the intrinsic resilience potential of storage systems
Currently, storage protection solutions primarily focus on safeguarding data integrity and availability. In the event of an attack, backup and archiving mechanisms help restore data access quickly, minimizing losses. However, these solutions have limitations in protecting data confidentiality. While disk encryption effectively prevents data breaches resulting from media theft, most data breaches or damage in current attack scenarios stem from vulnerabilities in cybersecurity, host operating systems, or service access controls. Once an attacker gains legitimate access permissions, they can extract data directly from the storage system.
There are two approaches we can use to solve this problem:
Approach 1: Creating an independent authentication mechanism that operates separately from the host access control list. This can be achieved by implementing an attribute-based access control (ABAC) mechanism within the storage system. Factors such as data access time, remote attestation results of servers, network packet loss rates, and packet delays can be analyzed to determine whether data access should be granted. When combined with a storage client agent deployed on the host, this approach enables more granular and refined access control. For example, it allows for fine-grained access management for sensitive data, or restricting access to specific directories for particular applications or processes.
Approach 2: Comprehensive attack detection systems. Currently, comprehensive ransomware detection solutions, including response and recovery measures, have been developed for the storage system. Moving forward, attack detection capabilities need to address a broader range of attack types. This involves mining data features to predict storage-related attacks and refining detection algorithms to analyze insider behavior. Combined with expanding the scope of ransomware protection in storage solutions outlined in Direction 1, this approach will enable a multi-dimensional analysis of attacks targeting hosts and networks, significantly improving the detection of data theft.
Direction 3: Improving the defensive capabilities of storage and data resilience solutions
Currently, storage systems are primarily targeted by attacks focused on hosts and servers. Once an attacker gains access to these devices, they can exploit legitimate read and write operations to compromise data in the storage system. However, advancements in storage resilience technologies are poised to change this. In the future, it will be harder for attackers to damage data even after they have compromised hosts and servers.
To adapt, attackers may adopt more sophisticated strategies, such as penetrating storage systems to disable protection mechanisms, clearing the way for malicious activities.
Given this, it is crucial to reevaluate the security design of the storage system to ensure that protection mechanisms for high-security data remain effective even if the storage system is compromised (e.g., an attacker gains access to a privileged account). High-security protection mechanisms are typically built on hardware features, which inevitably impact read and write performance. As a result, it is impractical to apply such protection to all data. A classified and hierarchical data protection approach, based on storage resilience and system architectures, is essential. Ideally, protection levels should align with data classification and the security risks involved, providing enhanced anti-attack capabilities for high-value data and critical services.
Another approach to strengthening the anti-attack capabilities of storage systems is by enhancing disk-level resilience. Even if storage software is compromised and an attacker gains full permissions, data can remain secure if the disks themselves can block malicious operations. The industry has already introduced ransomware detection disks, which is a significant step in this direction.
That's all from me for now—I look forward to sharing more insights on this topic in the future.
Source: Data Dialogue (2025 Jan. issue)